Using Optimize in BricsCAD, you can fix scanned drawings, Point Cloud drawings, or drawings created by tracing over existing images. Additionally, you can use this tool to straighten skewed lines and close gaps between lines, polylines, and arcs. It will also reduce file size and save manual work.
Optimize can be used in both 2D drawings and 3D models. In this article, we will look at how you can optimize your 2D drawings in BricsCAD V22.
Manual Tracing an Existing Image
Optimize is especially useful when you create a drawing by manually tracing over another image. To see how Optimize will fix the issues with our traced image, first select a raster image from your computer, like in the example below.

Once the image is loaded, you can create lines using the Line command in the Home tab. You can see where this is in this example.

Now that the line command is active, you can trace over the existing lines in the drawing you have open. In the image below, you can see this in action.

In the next step of the example, we create the diagonal in the traced image.

When you finish tracing the part of the drawing you need, you can erase the image you have loaded and see the results of your tracing.

Optimizing a Traced Image
Chances are, when you trace an image using this method, your new drawing won't be perfect. You can see the results in the image below. Some lines are straight like we expected, but others are skewed, and there are gaps between some of the lines.

Optimize can fix these types of issues in your drawings. It will close the gaps between the lines and straighten the skewed lines, and you can use it on arcs and polylines as well.
There are two ways to invoke the Optimize command. You can enter it in the command line using the keyboard. You can see how to do this in the example below.

The other way to access the Optimize command is by clicking on the Optimize tool in the Drawing Optimizations panel. You can find this in the Manage tab of BricsCAD.

Once you click on Optimize, BricsCAD will select all the entities in your drawing that can be optimized and give them a blue color. You will also get an optimization panel that will remain active while you use the command. You can see this in action in this next image.

2D and 3D Modes
Optimize command rectifies the line segments to align with the coordinate system axis and connect gaps between the line and arc segments in 2D, or it rectifies the faces to align with the coordinate system plane in 3D.
In the optimization panel, you see two modes for Optimize: 2D and 3D. In our example, the toggle for these modes is disabled because it works in 2D mode, and there are no 3D solids currently in the drawing.

To activate this toggle, you need to add a 3D solid to the drawing, as you can see in the image below. Now we can use Optimize in either 2D or 3D mode.

Entity Selection
In the optimization panel, you will find two options for selecting entities to be optimized: either the entire drawing or entities within the drawing. In our example, the entire drawing option is selected, so all non-frozen entities get selected.

When you choose the select entities option, you can manually select which entities will be optimized.

Reference Angles and Angle Tolerance
You will also see three options for the reference angle in the optimization panel:
horizontal
vertical
diagonal
Horizontal and vertical correct near horizontal and vertical lines according to how you set the angle tolerance. Diagonal will correct angles that are close to 45 degrees to 45 degrees.

You can set the angle tolerance in the Tolerance section below that. In our example, we have an angle tolerance of 5 degrees, so it will correct lines that are within 5 degrees of horizontal, vertical, or 45 degrees.

Merging Lines and Distance Tolerance
To merge parallel lines that are close to each other, you can use the distance tolerance setting. Parallel lines within the distance you set here will be merged.

In our example drawing, the area in the image below will be corrected if the distance tolerance setting is set correctly. To determine the distance, you can cancel Optimize and measure it.

Then go back to Optimize and set the distance tolerance to a higher value.
Closing Gaps and Gap Tolerance
If you check the close gap option in the panel, Optimize will close the gaps in the drawing's lines and arcs.

This setting is dependent on the gap tolerance setting, which you can see in the image below.

We can close a gap like this one in the example image, similar to how we merged lines. First, measure the distance of the gap.

Then set the gap tolerance to a distance higher than the distance you measured, and the gap will be filled.
Feedback
In the feedback area of the optimization panel, you will find information relating to what will be optimized in your drawing. In our example, it tells us that seven of the entities in the drawing are highlighted and will be optimized, and all the selected entities will be flattened.

Preview, Reset, and Keep Selection
At the very bottom of the optimization panel, you can click on the Preview button, and BricsCAD will apply all the settings and you can see the results. In our example below, lines are perfectly horizontal and vertical, the diagonal line is right at 45 degrees, parallel lines are now collinear, and the gaps in the drawing are gone.

Clicking the Reset button when you are previewing will cancel all the settings and reset your drawing.

The Keep Selection button will turn off Optimize but leave all entities selected.

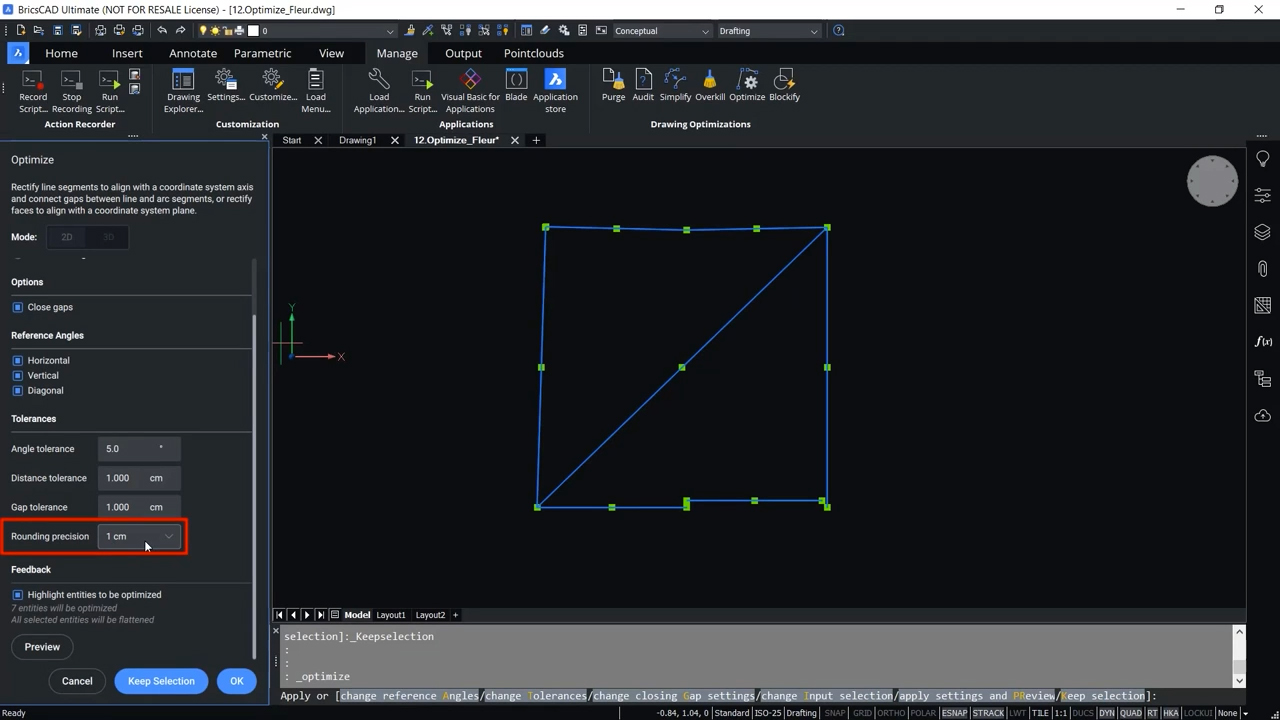
Rounding Precision
Another setting in the Tolerance section of the optimization panel is rounding precision. The entities in a drawing will be rounded off to the closest multiple of this value when they are optimized.

In the example above, there is a rounding precision of 1 centimeter, and if we examine the drawing, all sides of the entity are in whole centimeters.

If we set the rounding precision to 0.1 centimeters and check the measurements of the drawing again, they have changed and now include a decimal.

Optimize is a BricsCAD command that can clean up your drawings by closing gaps, merging lines, and making sure lines are horizontal, vertical, or diagonal, and it can save you a lot of time. To find out more about this command, watch the full video this article is based on.